Recognizing and First Aid for Venomous Snake Bites: Detailed and Correct Instructions
Every rainy season, especially in tropical regions, the number of patients bitten by venomous snakes often increases significantly. Improper first aid can lead to serious complications such as limb necrosis, blood poisoning, and even death. To minimize risks and save victims, recognizing venomous snakes and providing timely first aid is extremely important.
1. Common Venomous Snakes
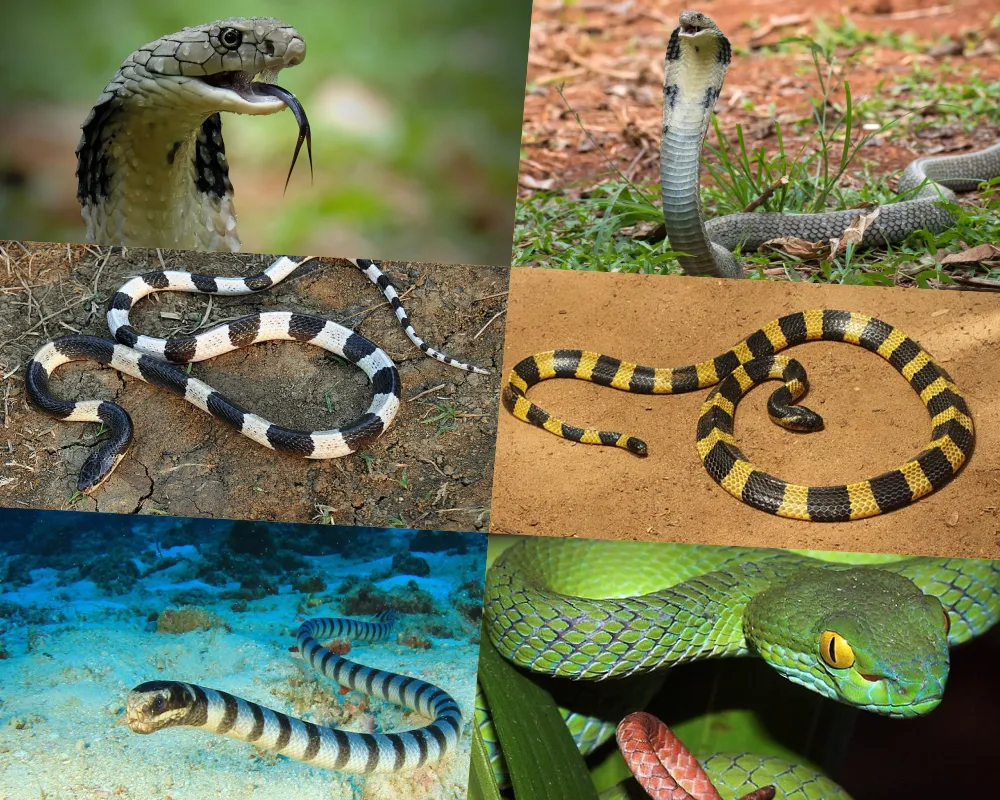
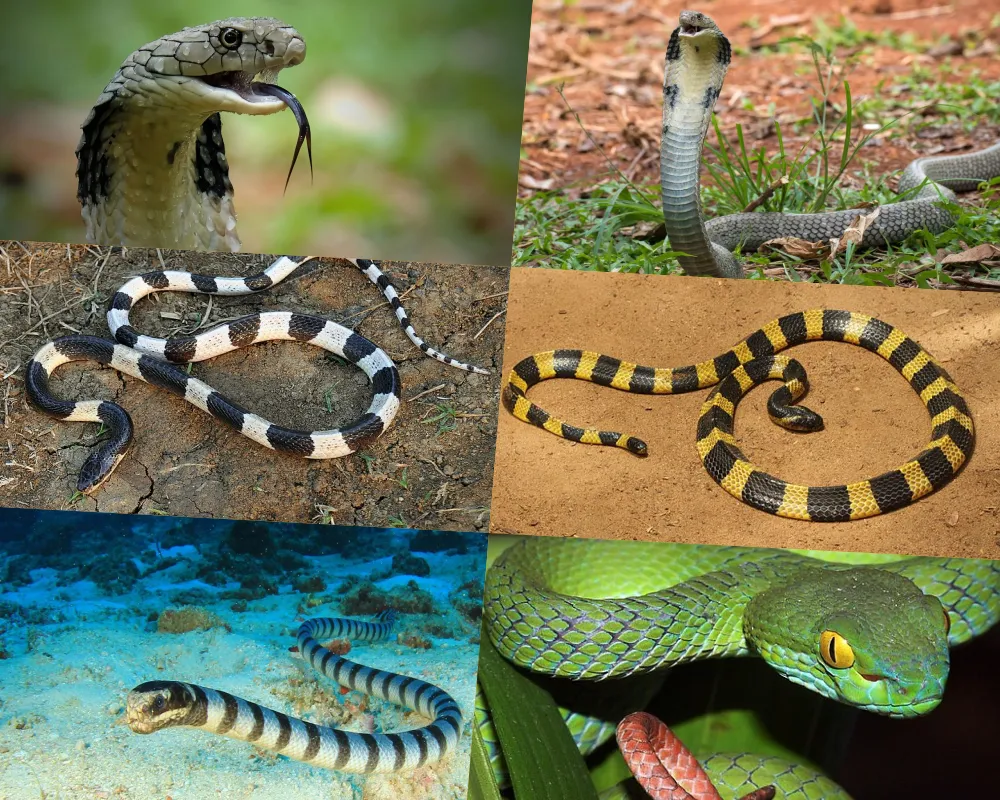
Cobra Family
- Cobra:
– Common Cobra : (including cobras, banded cobras, puffed cobras, and cat cobras) have a bulging neck and emit a characteristic sound when threatening. They often live in mountainous areas, midlands, plains, and even near residential areas.
– King Cobra : Large in size, weighing tens of kilograms, usually longer than 2.5m. The neck is wide but not wide, with two large scales on the top of the head. They live in the mountains and are now raised in many places. - Scorpion :
– Scorpion: Body has black-yellow bands.
– Scorpion: Body has black-white bands. Usually lives in the midlands, plains, and areas near water. - Sea Snake: A type of venomous snake that lives mainly in coastal areas.
- Symptoms of Poisoning:
– At the Bite Area: Pain, swelling, possible necrosis of the skin, infection with redness, fever, and pus.
– Whole Body: Severe pain, difficulty speaking, blurred vision, weak limbs, difficulty breathing, paralysis of the whole body, arrhythmia, little urine, … There is a high risk of death due to muscle paralysis causing difficulty breathing.
Viper Family
- Green Viper : Green, usually lives in mountainous forests in all regions.
- Dry Wood Viper, Snub-nosed Viper : Brown body or like dry tree branches, usually lives in mountainous forests in the North.
- Crowning Viper : Brown body, usually lives in southern forests.
- Symptoms of Poisoning :
– At the Bite Area : Swelling, blisters, bleeding at the bite area, and difficult-to-stop bleeding throughout the body. Risk of death due to blood loss and internal bleeding.
2. How to Identify Venomous and Non-Venomous Snakes
- Physical Characteristics :
– Cobra : Neck flares when threatening, makes a characteristic sound.
– Kracoon : Body has black-yellow stripes.
– Kracoon : Body has black-white stripes.
– Viper Family : Triangular or diamond-shaped head. - Characteristic Bites :
– Venomous Snake : Has two large poisonous fangs (poisonous hooks) located in the upper incisors, leaving a characteristic bite mark.
– Cobra : Can spray venom that can damage the eyes.
3. First Aid for Snake Bites
Objectives of First Aid
– Remove venom and slow its movement.
– Protect life and promptly treat complications.
– Transport the patient safely to a medical facility.
– Avoid further harm to the patient.
First Aid Steps to Take
– Reassure the Patient: Keep calm, do not let the patient move.
– Immobilize the Bitten Area: Use a splint to immobilize the bitten leg or arm.
– Remove Jewelry: To avoid compression due to swelling.
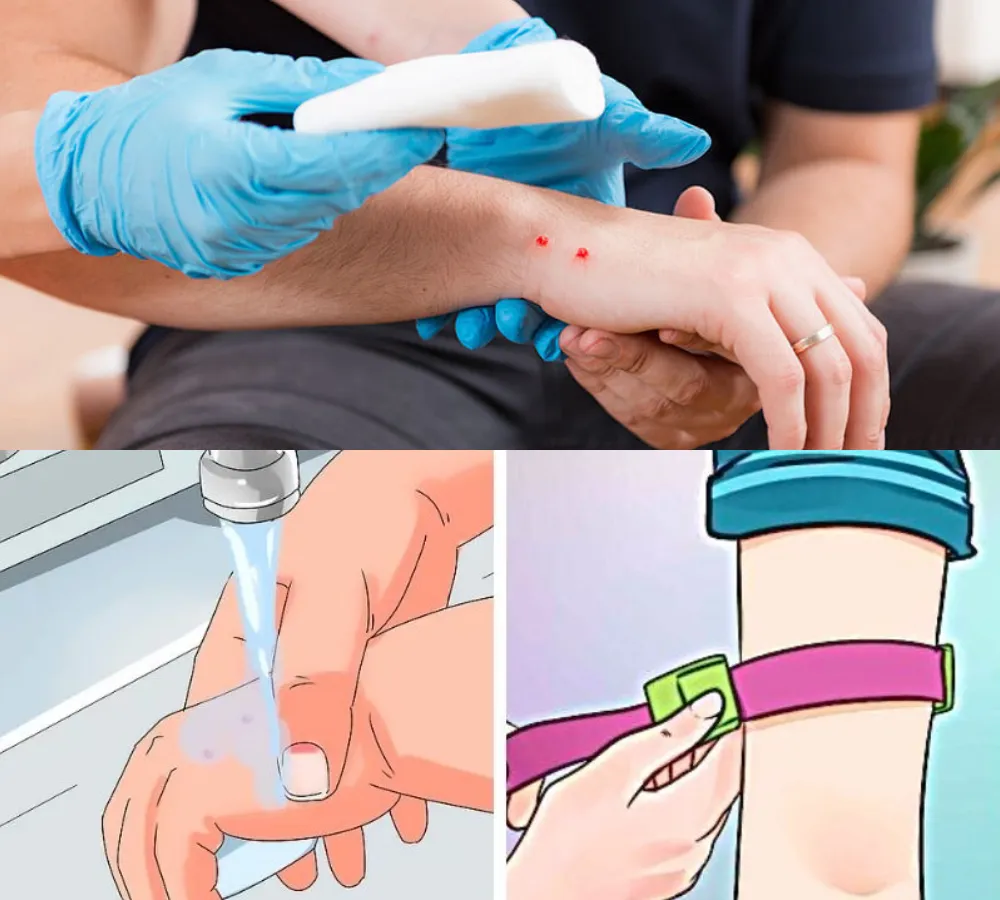
– Apply Immobilizing Bandage: Only applicable to some types of cobras, do not apply pressure to vipers.
– Wash the Bite: Under clean running water with soap and antiseptic.
– Artificial Respiration: If the patient has difficulty breathing or has stopped circulating.
– Transport Immediately: Go to a medical facility, maintain pressure and keep the bitten area lower than the heart.
Do Not Use the Following Measures
– Tournament: Dangerous, can cause anemia and amputation.
– Pricking, Incision, Puncture: Causes further harm to the patient.
– Suction of Venom: Ineffective.
– Ice Pack: May cause further harm.
– Use of Traditional Medicine: Not helpful, can cause infection.
– Catch or Kill the Snake: Take the snake to the hospital for identification if possible.
4. Snake Bite Prevention
– Know the Snake: Know the area and characteristics of snakes.
– Protective Equipment: Wear boots, high-top shoes, long pants, and a wide-brimmed hat when outdoors.
– Avoid Near Snake Areas: Do not live near places where snakes like to live.
– Use Lights When Walking at Night: To easily detect and avoid snakes.
Proper awareness of venomous snakes, symptoms of poisoning, and first aid procedures will help minimize risks and increase the chances of survival when bitten by a snake. Always take the patient to a medical facility for timely and effective treatment.







