Pavel Durov’s recent arrest has ignited a debate over encryption technologies, highlighting the differing approaches between messaging apps and raising concerns among tech leaders in Silicon Valley.
Pavel Durov, the founder of the popular messaging app Telegram, is at the heart of a legal storm that has captured the attention of tech executives worldwide. The French authorities’ arrest and subsequent charges against Durov have sparked significant controversy, particularly concerning the encryption technology employed by Telegram.
The crux of the matter revolves around Telegram’s use of encryption—a topic that has become a focal point of concern for many tech leaders, including those from Signal, Apple, and WhatsApp. These companies provide end-to-end encryption, a security feature that ensures messages are only accessible to the sender and receiver, with no interference or data theft possible. As a result, such encryption is seen as a crucial component in safeguarding everyday communications.
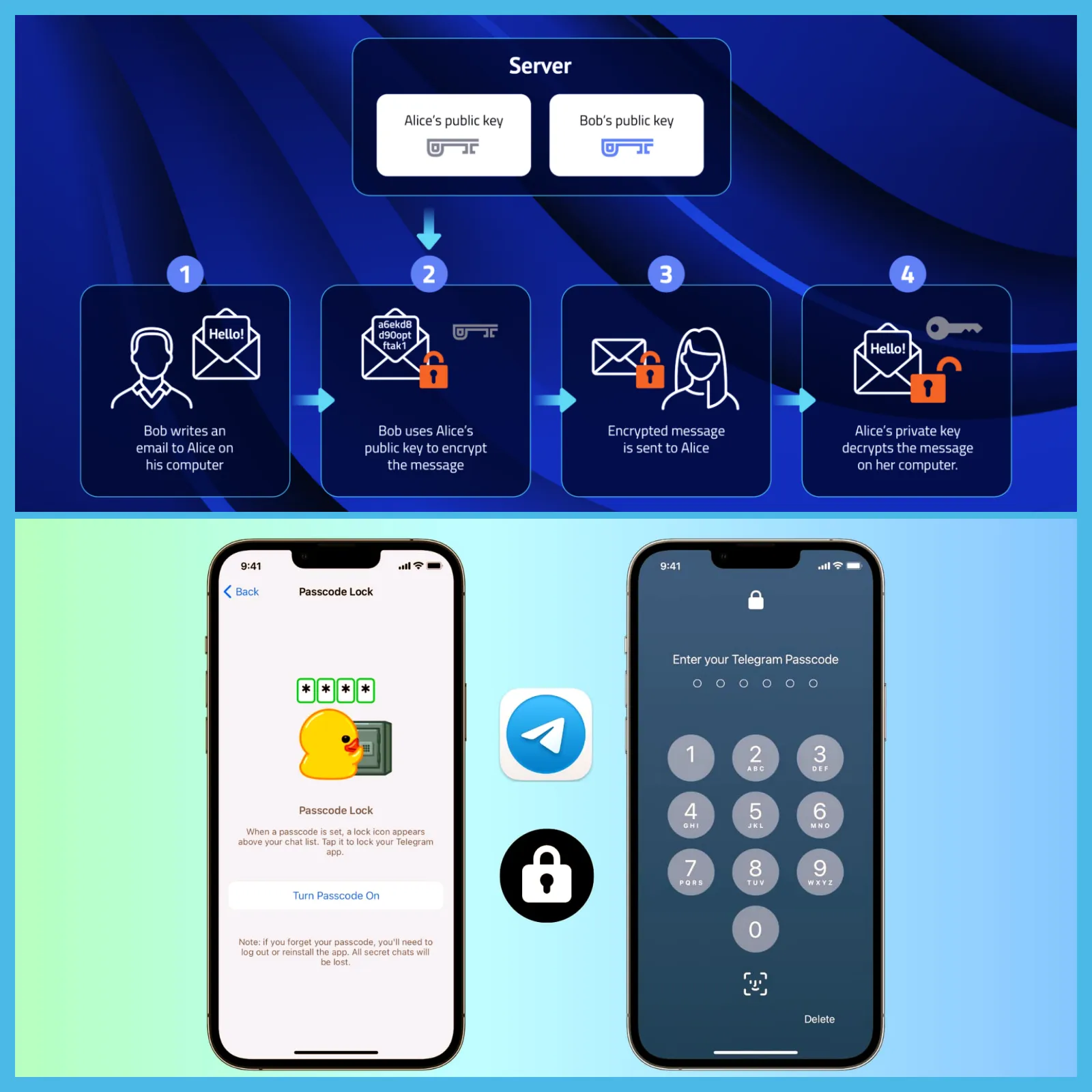
However, Telegram’s approach to encryption differs from that of its competitors. Unlike WhatsApp, Signal, and iMessage, Telegram’s encryption features are not enabled by default. Instead, users must manually activate the “secret chat” feature for end-to-end encryption, and this option is only available for one-on-one conversations, not group chats. This configuration has raised questions about the robustness of Telegram’s encryption, especially since its methods are not as transparent as those of Signal, which openly shares its encryption protocols for scrutiny.
The controversy intensified when French officials accused Telegram of operating without proper authorization for its encryption services. This has led to fears among Silicon Valley executives that Durov’s legal troubles could cast a shadow over the entire encrypted messaging market. Daphne Keller from Stanford’s Center for Internet and Society highlighted these concerns, stating that if Durov’s case is perceived as a failure of encryption technology, it could tarnish the public image of encrypted messaging apps overall.
The encryption debate has long been a contentious issue between technology companies and governments. While tech firms argue that encryption is vital for digital privacy, authorities contend that it can shield criminal activities from investigation. This tension has only grown as more users embrace encrypted messaging platforms. For instance, Signal, which has tens of millions of users since its 2018 launch, Apple’s iMessage, and WhatsApp, with its 2 billion global users, all rely on end-to-end encryption to secure communications.

Past legal battles have shown how fiercely tech companies defend their encryption practices. WhatsApp threatened to cease operations in the UK if new laws compromised its encryption. Signal’s Meredith Whittaker vowed to exit the UK market if proposed regulations undermined its security features. Apple refused to disable iMessage encryption for the FBI, despite demands related to a high-profile investigation.
The European Union is also considering legislation that would require online messaging services to scan for harmful content, potentially impacting encryption standards. This development has alarmed privacy advocates who fear that public sentiment may lean towards supporting stricter regulations for the sake of child protection.
As Durov faces accusations not only of operating unauthorized encryption but also of aiding criminal activities, including child exploitation and drug trafficking, the situation remains fluid. Durov is currently banned from leaving France, and his case is stirring debate about whether Telegram’s less stringent encryption standards contributed to its legal challenges.
Zach Judge-Raza, a data privacy lawyer, suggests that Telegram’s lack of default encryption might be a key factor in its legal woes, as it allows for more visibility of shared content compared to competitors.
With Durov at the center of this controversy, it’s likely that Silicon Valley tech giants will rally in defense of encryption technologies, possibly even supporting Telegram’s controversial approach as a means to uphold their own encryption practices.






